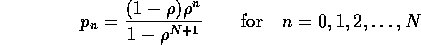
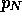 is the
probability that the buffer is full at an arbitrary point in time.
is the
probability that the buffer is full at an arbitrary point in time.
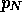 =
=
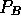 =
probability an arriving packet is turned away due to a full buffer.
=
probability an arriving packet is turned away due to a full buffer.
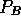 is called the
blocking probability.
is called the
blocking probability.
 is very important!
is very important!
 to choose
the correct buffer size.
to choose
the correct buffer size.
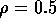 ,
,
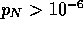 for N=18,
while
for N=18,
while 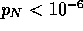 for N=19.
for N=19.
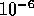 , we need
a buffer capable of holding 19 packets.
, we need
a buffer capable of holding 19 packets.