11/24/2002
Noise: An Introduction
9
Probability Distribution
continued
continued
•The actual equation
is: P(vn) = ˝ + (1/p)arcsin(v/A)
•Note that the noise
spends more time near the extremes and less time near zero. Think
of a pendulum:
–It stops at the
extremes and is moving slowly near them
–It move fastest at the
bottom and therefore spends less time there.
•Another useful
function is the derivative of P(vn):
the
“Probability Density Function”, p(vn) (note the lower case p)
“Probability Density Function”, p(vn) (note the lower case p)
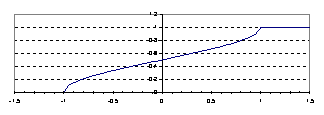
Shown for A=1